We keep Timing belt kits in AE, Dayco, FAI, INA & Gates
Trouble Tracer Chart
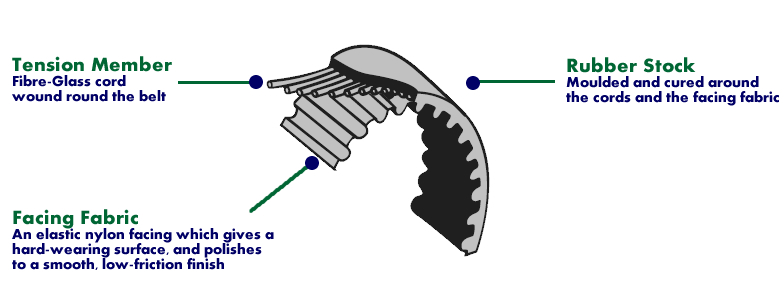
SYMPTOMS
Failure: A few popular engines are designed such that the valves when fully open will not contact the piston at top dead centre. Cam belt breakage will stop the engine but should not cause any damage. However, on most engines, timing belt failure results in major damage. These are called "interference engines". Valve to piston contact often occurs requiring replacement of valves, valve guides, camshaft pistons, and possibly cylinder head and block repair.
SERVICE TIPS
Do not refit a timing belt. Engine manufacturers specify the tension to which a new belt should be set. In operation however, the tension will relax slightly to a lower value. If a used belt was refitted, and tensioned to the manufacturer‘s figure for a new belt, it would run too tight in use. As it is almost impossible to refit a belt to the tension it ran at before removal, it is recommended that belts should never be refitted. Change your belt at the interval specifi ed by the vehicle manufacturer. Due to the constant flexing the fibres of the tension cords eventually fatigue, and break. The life of a belt depends upon many factors including: the tensile forces it transmits, its width, its overall length, the design of the cords, the size of the pulleys and the torsional vibration characteristics in the engine. The manufacturers replacement period has been established so that a belt is renewed before the fatigue may cause it to fail, and should be adhered to.Storage of timing belts. Timing belts are rubber composite products and as such should be stored away from sunlight, oil, water and solvents. They should not be crushed or bent tightly, for example by hanging on a peg.
GENERAL REMEDY
All failures require the engine to be rebuilt to the manufacturers specification replacing all damaged components. In particular, ensure that:• The belt is correctly tensioned.
• The tensioner mechanism operates correctly and is properly secured.
• All idler wheels and auxiliary shafts rotate freely.
• The gears are clean, undamaged, and in alignment.
• The enclosure is in good order.
• Any oil leakage into the enclosure has been stopped.
|
Foreign Body Entrapment
|
|
 |
Symptom: Belt breakage, in a |
|
Edge Wear
|
|
 |
Symptom: Excessive wear and |
| Land Wear | |
 |
Symptom: Wear, or polishing, |
| Tooth Peel | |
 |
Symptom: Teeth peeling, emanating |
| Tooth Sheer | |
 |
Symptom: Six or more teeth
missing, often with cracking in roots of a number of teeth. Cause: May be due to sudden overload of the drive from the seizure of a driven part, such as a water pump. Also may be due to low tension, which allows the belt to ride high on the gear, producing excessive bending moments, and defl ection of the teeth until cracks form. Remedy: Ensure all driven items rotate smoothly.Set new belt to correct tension and ensure tensioner mechanism is tight. |
| Tooth Wear | |
 |
Symptom: Hollows through
the facing fabric. Cause: Extremely low tension allows the belt to ride out on the gear, causing localised wear on edge of the thrust face. Sometimes excessive tension, pulling the belt up the land, may wear the tooth face, before a tensile failure. Remedy: Set new belt to correct tension and ensure tensioner mechanism is tight. |
| Oil Contamination | |
 |
Symptom: Dirty or smelly belt,
with a ragged decomposing structure. Cause: Contamination from a failed oil seal, or an oil or diesel leak, breaks down the adhesion of the rubber. Swelling can also occur and cause mismeshing leading to other types of failure. Remedy: Ensure oil leak is stopped. Check belt enclosure and dust shields. Set new belt to correct tension and ensure tensioner mechanism is tight. |
| Tensile Failure | |
 |
Symptom: Tensile breakage,
with a straight break between two teeth. Cause: Some of the tensile cord‘s fi bres have broken due to crimping (folding) before or during assembly, creating a weak point. A belt running over-tensioned may sometimes cause teeth to ride up onto gear lands, resulting in vast over stretching and tensile failure. Remedy: Replace belt carefully, without pinching or levering. Set new belt to correct tension and ensure tensioner mechanism is tight. |
| Back Cracks | |
 |
Symptom: A series of cracks
across the back of the rubber stock. Cause: The rubber has been over-heated and has degraded, possibly from friction on a seized idler or water pump. Extreme cold may have the same effect. Remedy: Ensure all spindles driven off the back of the belt, including water pumps, rotate freely. Set new belt to correct tension and ensure tensioner mechanism is tight. |

